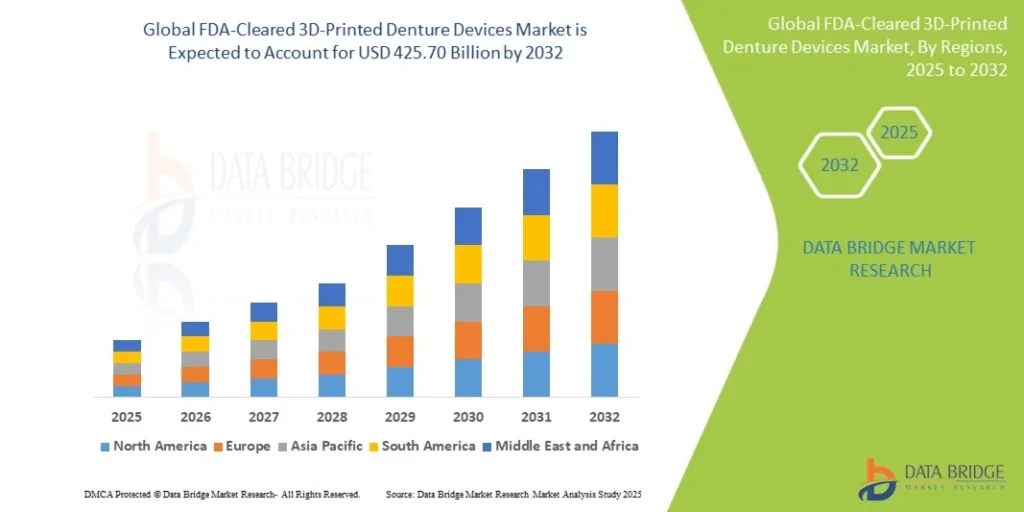
The FDA-Cleared 3D-Printed Denture Devices market was valued at USD 178.20 Million in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 425.70 Million by 2032, growing at a CAGR of 11.5% (2024-2032). Get insights on trends, segmentation, and key players with Data Bridge Market Research Reports.
Introduction
The dental world is changing fast. One of the most significant shifts over the last decade is the rise of 3D printing – and it’s not just for prototypes. Today, fully functional denture devices manufactured with 3D printers are being used in clinics worldwide. When these devices receive FDA clearance, they move from being interesting experiments to trusted treatment options. This guide explains what FDA-cleared 3D-printed dentures are, how they’re made, who they’re right for, potential benefits and trade-offs and what the future may hold.
Definition
FDA-Cleared 3D-Printed Denture Devices are dental prosthetics manufactured using additive manufacturing (3D printing) technologies that have received clearance from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for safe and effective use in replacing missing teeth. These devices are produced from biocompatible materials and validated digital workflows that meet FDA standards for strength, fit, durability and patient safety, ensuring they perform comparably to conventionally made dentures.
What “FDA-Cleared” Means for 3D-Printed Dentures
“FDA-cleared” signals that a device has gone through regulatory review and the agency has determined it is substantially equivalent to an already-marketed device (a predicate). For denture devices, this typically means the materials, manufacturing process, and intended use were examined for safety and effectiveness for patients. Clearance differs from FDA approval (which is a stricter process used for higher-risk devices), but clearance still provides an important assurance: the product meets regulatory expectations for clinical safety and device performance.
How 3D-Printed Dentures Are Made
The workflow for modern 3D-printed dentures generally includes these steps:
- Digital impression/scanning: Instead of traditional physical impressions, a clinician uses an intraoral scanner or scans a cast to create a precise digital model of the patient’s mouth.
- Digital design (CAD): Technicians use CAD software to design denture bases, tooth setups, and occlusal relationships tailored to the patient.
- 3D printing: The denture base or even entire denture (base + teeth) is printed using biocompatible resins or specialized dental polymers in an additive process (SLA, DLP, or material jetting).
- Post-processing: Printed parts are cleaned, cured, and often polished. Where necessary, teeth may be bonded or finished manually.
- Quality checks: Dimensional accuracy, fit, and surface finish are evaluated. For FDA-cleared products, manufacturers follow validated processes and documentation.
- Delivery and adjustments: The denture is fitted to the patient; minor adjustments are typically similar to conventional dentures.
Materials and Biocompatibility
Materials for 3D-printed dentures are formulated for strength, wear resistance, and biocompatibility. Typical materials include dental-grade photopolymer resins and specialized thermoplastics engineered for long-term use in the oral environment. FDA-cleared materials will have evidence backing their safety (e.g., cytotoxicity testing, wear studies, and leachables analysis) and are intended for intraoral use.
Benefits of FDA-Cleared 3D-Printed Dentures
- Precision and fit: Digital capture and additive manufacturing can produce exceptionally accurate, reproducible fits, reducing adjustment time.
- Speed: Digital workflows often shorten turnaround times — in some settings, same-day or next-day dentures are feasible.
- Customization: Digital design allows precise occlusal setup, esthetic customization, and easier replication of prior prostheses.
- Reproducibility and documentation: Digital files mean you can reprint a replacement denture from the same design if the original is lost or damaged.
- Potential cost efficiencies: For labs and clinics that adopt digital workflows, per-case production time and labor can drop, sometimes lowering costs for patients over time.
Who Is a Candidate?
Most patients who need complete or partial dentures and have a reasonably healthy oral environment can be candidates. Factors that influence candidacy include:
- Condition of the residual ridges and oral tissues.
- Presence of implants (for implant-supported overdentures).
- Patient expectations for esthetics and function.
- Ability to follow care instructions.
Clinicians still evaluate bone anatomy, soft tissues, and occlusion – the same fundamentals used for conventional dentures apply.
Clinical Considerations & Workflow Tips
- Digital scanning skill matters: Accurate scans are foundational; poor scans lead to poor fits regardless of printing quality.
- Laboratory communication: Clear instructions and collaboration between clinician and lab improve outcomes, especially for shade selection and tooth setup.
- Post-printing finishing: Surface polishing and proper curing are essential to reduce roughness that could harbor plaque.
- Try-in options: Some workflows support a printed try-in (in a different, low-cost material) so esthetics and occlusion can be confirmed before final printing.
- Maintenance: Patients should be instructed on cleaning printed materials using non-abrasive cleaners and routine dental follow-ups.
Limitations & Risks
- Material longevity: While many resins are durable, long-term wear characteristics are still evolving compared to traditional heat-cured acrylics in some cases; patients may experience different wear patterns.
- Repairs: Repairing a 3D-printed denture can be different than repairing conventional materials – labs may need specific protocols.
- Cost of equipment: For practices or labs, initial investment in scanners, software, and printers can be substantial even if per-unit costs fall over time.
- Regulatory compliance: Using an FDA-cleared material/device requires adherence to the intended use and validated manufacturing steps; deviations can affect safety and regulatory standing.
The Future: Where This Technology Is Headed
Expect continual improvements in materials, multi-material printing (combining resilient bases with harder occlusal surfaces), and software-driven design algorithms that optimize fit and function. As clinical evidence grows and more products gain FDA clearance, digital denture workflows will become even more mainstream – improving access, customization, and patient satisfaction.
Choosing an FDA-Cleared Product or Provider
When selecting a manufacturer, lab, or clinic offering 3D-printed dentures, consider:
- Whether the product is FDA-cleared for the specific denture use.
- Clinical data demonstrating fit, wear resistance, and biocompatibility.
- The lab’s experience with digital workflows and post-processing protocols.
- Warranties or guarantees for fit and replacements.
- Patient reviews and before/after cases you can review.
Future Trends of FDA-Cleared 3D-Printed Denture Devices Market
Advancements in Printing Materials:
Next-generation biocompatible resins and hybrid polymers are being developed to enhance durability, aesthetics, and wear resistance. These materials will enable longer-lasting dentures that closely mimic natural gum and tooth structures.
Integration of AI and Automation:
Artificial intelligence is increasingly being integrated into denture design software, automating occlusal alignment, tooth arrangement, and digital try-ins. This trend will reduce human error, speed up production, and improve customization accuracy.
Expansion of Multi-Material 3D Printing:
Future printers will support multi-material fabrication – allowing simultaneous printing of flexible bases and hard tooth components – reducing assembly time and improving overall fit and comfort.
Growth of Chairside 3D Printing:
As compact and affordable dental printers enter the market, more clinics will adopt chairside manufacturing. This will enable same-day denture delivery and increase patient satisfaction while reducing dependence on external labs.
Growth Rate of FDA-Cleared 3D-Printed Denture Devices Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the FDA-Cleared 3D-Printed Denture Devices Market was estimated to be worth USD 178.20 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 11.50% to reach USD 425.70 million by 2032.
Learn More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-fda-cleared-3d-printed-denture-devices-market
Conclusion
FDA-cleared 3D-printed dentures represent a meaningful advance in prosthodontics: they combine digital precision with regulatory oversight to deliver fast, customizable prostheses that meet safety standards. While not a universal replacement for every conventional technique, they are a powerful option for many patients and clinics. If you’re considering 3D-printed dentures, talk with your dentist or prosthodontist about product specifics, expected longevity, and whether a digital workflow is appropriate for your needs — and always confirm that the device and materials used are FDA-cleared for the intended denture application.





